🧮 Constant Difference
✅ Concept: When the difference between two quantities stays the same even after changes (e.g. both increase or decrease by the same amount), we use the Constant Difference method.
💡 Tip:
- Useful for solving word problems with same increase/decrease.
- Use when both parties change by the same amount.
🧩 Example Problem:
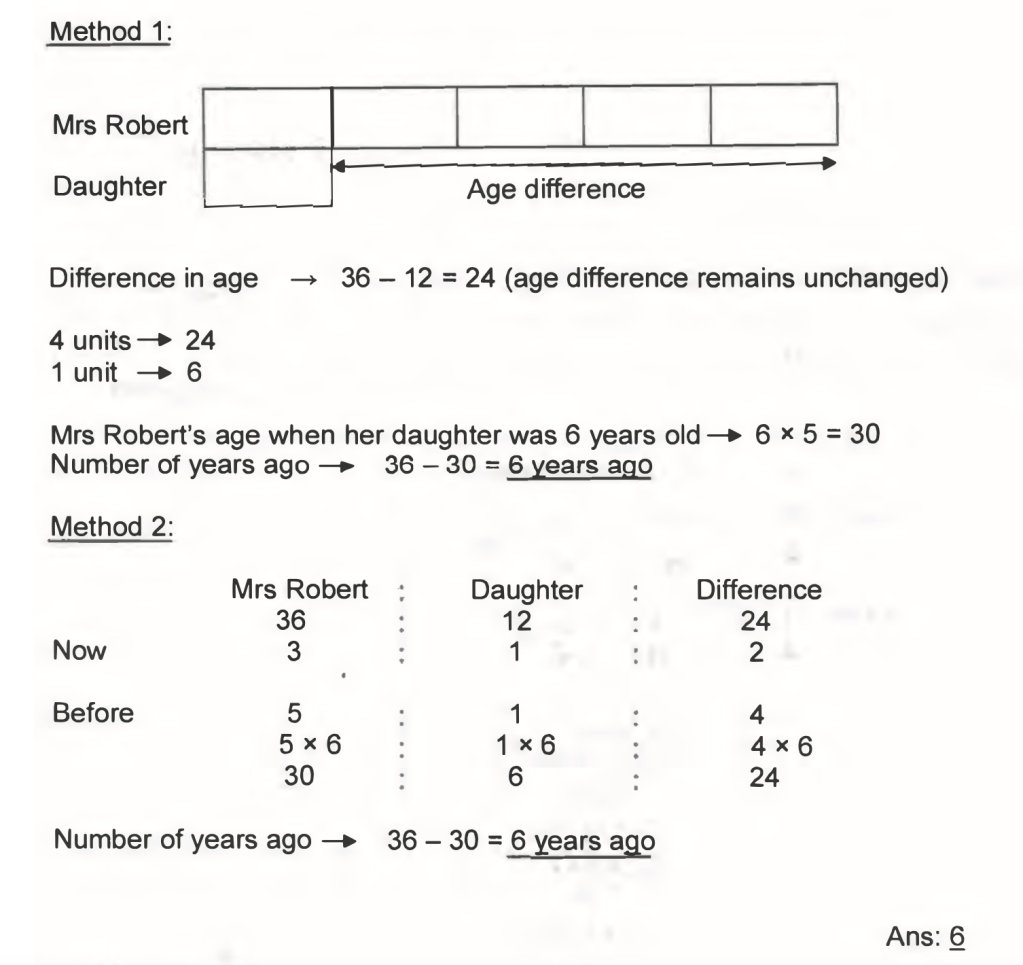
Mrs Robert is 36 years old and her daughter is 24 years younger.
How many years ago was Mrs Robert five times as old as her daughter?
🧠 Step-by-Step Breakdown:
When a question involves a comparison of ages and phrases like “How many years ago…”, think:
👉 Constant Difference strategy.
That means:
✅ The age gap never changes.
✅ Only time moves forward or backward equally for both.
🧮 Proportion / Grouping
✅ Concept: Use this when items or people are grouped equally or compared in ratios.
💡Tip:
- Look for words like “each”, “per group”, “shared equally”.
- Sometimes involves ratio or unitary method.
🧩 Example Problem:
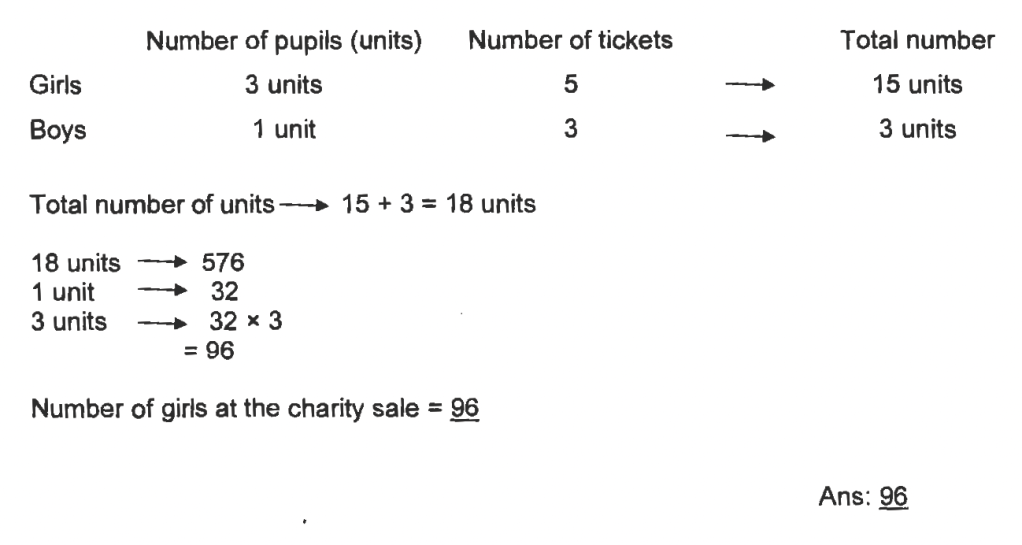
For a school charity sale, every girl was given 5 tickets to sell and every boy was given 3 tickets to sell.
There were thrice as many girls as boys at the sale.
If a total of 576 tickets were sold, how many girls were at the charity sale?
🧠 Step-by-Step Breakdown:
When you see keywords like:
- “Every boy/girl gets ___”
- “There are ___ times as many of one group as another”
- “Total = ___”
👉 You’re in Grouping and Proportion territory!
–
🧮 More Than / Less Than (with internal transfer)
✅ Concept: Involves transfer of items between two parties. The total stays the same, but one has more/less than before.
💡Tip:
- Great for “equal number” after giving/sharing problems
🧩 Example Problem:
The number of marbles in container A was 36 more than that in container B.
When 48 marbles were removed from container A and placed in container B, the number of marbles in container B became thrice that of container A.
Find the number of marbles in container A at first.
🧠 Step-by-Step Breakdown:
When you see phrases like:
“Internal transfer” = giving between two people, no new items added
Use difference ÷ 2 to balance
- “A had more than B”
- “Then marbles were moved from A to B”
- “Now B has ___ times A”
👉 It’s time to use internal transfer logic – no marbles were lost, just moved!

🧮 More Than / Less Than (with comparison at two points)
✅ Concept:
Compare amounts at two different times. Track changes over time (e.g. “before” and “after”).
💡 Tip:
- Draw a table or model: Before → Change → After
- Be careful with words like “more than”, “less than”, or “now”
- Common in 2-point comparison or before-and-after problems
🧩 Example Problem:
There were three times as many men as women at the party at first.
After 18 men left and 10 women entered, there were 6 more men than women remaining.
Find the number of men at the party at first.
🧠 Step-by-Step Breakdown:
When you see:
- “There were ___ times as many…”
- “Then some left/entered…”
- “Now there are ___ more than…”
👉 You’re looking at a comparison at two time points, and it’s time to use algebra or model drawing!

Leave a comment